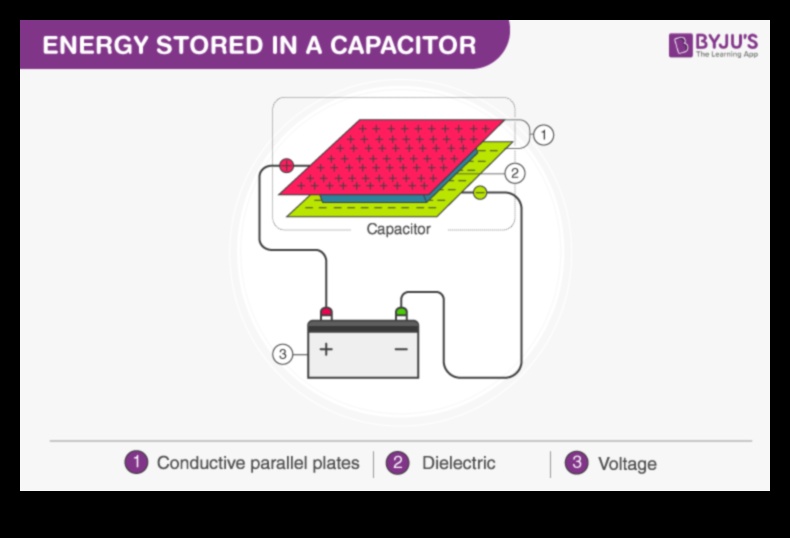
Capacitor Function
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field. It consists of two conducting plates separated by an insulating material. When a voltage is applied to the capacitor, the charges on the plates are separated, creating an electric field between them. The amount of charge that can be stored in a capacitor is determined by its capacitance, which is measured in farads (F).
Capacitors are used in a variety of electrical applications, including:
- Filtering noise
- Stabilizing power supplies
- Tuning radios
- Powering electronic devices
In electrical work, capacitors are often used to filter out unwanted noise from a signal. This is because capacitors can block high-frequency signals while passing low-frequency signals. This makes them ideal for use in applications such as audio amplifiers and radio receivers.
Capacitors can also be used to stabilize power supplies. This is because capacitors can store energy and release it when needed. This helps to smooth out the output of a power supply, making it more consistent.
Finally, capacitors can be used to tune radios. This is because capacitors can change the resonant frequency of an LC circuit. This allows radios to be tuned to specific frequencies.
Capacitors are an important part of many electrical applications. They are used to filter noise, stabilize power supplies, and tune radios. By understanding how capacitors work, you can use them to improve the performance of your electrical systems.
| Capacitor | Electrical Job/Work/Function |
|---|---|
| Stores Electrical Energy | Filters out unwanted frequencies |
| Stabilizes Voltage | Reduces Noise |
| Starts Motors | Synchronizes AC Circuits |
| Provides Timing | Protects Circuits |
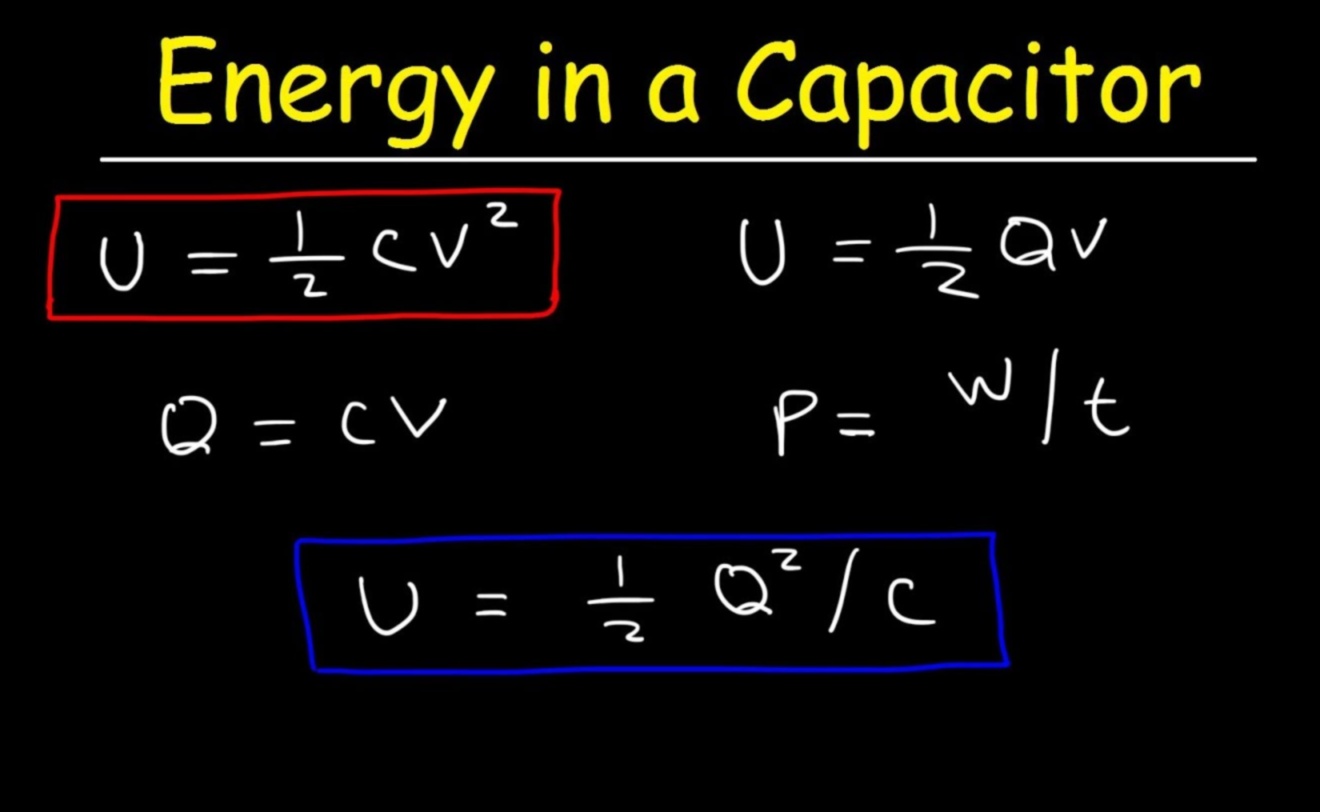
II. Capacitor Function
A capacitor is a passive electronic component that stores electrical energy in an electric field. Capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for a variety of purposes, including filtering, timing, and signal processing.
The basic principle of a capacitor is that it consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material. When a voltage is applied to the plates, an electric field is created between them, and the capacitor stores energy in the form of electrical charge.
The capacitance of a capacitor is measured in farads (F), and it is determined by the size and shape of the plates and the insulating material between them. Capacitors are available in a wide range of capacitance values, from a few picofarads (pF) to several million farads (MF).
Capacitors are used in a variety of electrical applications, including:
- Filtering: Capacitors can be used to filter out unwanted noise from a signal.
- Timing: Capacitors can be used to create delays in a circuit.
- Signal processing: Capacitors can be used to amplify or attenuate signals.
Capacitors are an essential component of electronic circuits, and they play a vital role in a wide range of applications.
III. Capacitor Function
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field. Capacitors are used in a wide variety of electrical applications, including power supplies, filters, oscillators, and timing circuits.
The basic function of a capacitor is to store charge. When a capacitor is connected to a power source, it charges up and stores the electrical energy in the form of an electric field. This stored energy can then be released when needed, such as to power a circuit or to provide a voltage boost.
Capacitors are also used to filter out unwanted signals from a circuit. For example, a capacitor can be used to filter out the high-frequency noise from a power supply. This is because capacitors block high-frequency signals while passing low-frequency signals.
Finally, capacitors are used in oscillators and timing circuits. An oscillator is a circuit that produces a periodic output signal, such as a sine wave or square wave. A capacitor is used in an oscillator to provide the feedback necessary to sustain the oscillation.
Capacitors are an important part of many electrical circuits. They are used to store energy, filter signals, and generate oscillations. By understanding the basic function of a capacitor, you can better understand how they are used in electrical circuits.
II. Capacitor Function
A capacitor is a passive electronic component that stores electrical energy in an electric field. It is a two-terminal device consisting of two conducting plates separated by an insulating dielectric. Capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for storing energy, filtering out unwanted signals, and creating timing delays.
The capacitance of a capacitor is measured in farads (F), and it is determined by the size of the plates, the distance between the plates, and the type of dielectric material. Capacitors are available in a wide range of capacitance values, from picofarads (pF) to farads (F).
Capacitors are used in a variety of electrical applications, including:
- Power supplies
- Signal processing
- Timing circuits
- Audio and video equipment
- Electrical motors
Capacitors are essential components in many electronic circuits, and they play a vital role in the operation of a wide range of electrical devices.
V. Capacitor Applications
Capacitors are used in a wide variety of electrical applications, including:
- Power conditioning
- Signal filtering
- Oscillators
- Power supplies
- Motor control
- Audio and video equipment
- Computers and other electronic devices
In power conditioning applications, capacitors are used to filter out noise and provide a smooth, consistent supply of power. In signal filtering applications, capacitors are used to block or pass certain frequencies of signals. In oscillators, capacitors are used to create a resonant frequency. In power supplies, capacitors are used to store energy and provide a smooth, constant output voltage. In motor control applications, capacitors are used to start and run motors. In audio and video equipment, capacitors are used to filter out noise and improve the quality of the sound. In computers and other electronic devices, capacitors are used to store data and provide power to the circuits.
Capacitors are an essential component of many electrical systems and devices. They play a vital role in ensuring the proper operation of these systems and devices.
VI. Capacitor Applications
Capacitors are used in a wide variety of electrical applications, including:
- Power factor correction
- DC to DC conversion
- Pulse width modulation
- Signal filtering
- Audio and video applications
- Motor starting
- Power supplies
- Uninterruptible power supplies
- Ripple suppression
For more information on capacitor applications, please see the following resources:
- Capacitor Applications (DigiKey)
- Capacitor Applications (Mouser)
- Capacitor Applications (Newark)
VII. Capacitor Ratings
Capacitors are rated according to their capacitance, voltage, and temperature. Capacitance is measured in farads (F), and the voltage rating is the maximum voltage that the capacitor can withstand without breaking down. The temperature rating is the maximum temperature at which the capacitor can operate without its capacitance changing significantly.
Capacitors are also rated according to their tolerance, which is the percentage by which the actual capacitance can vary from the specified value. Tolerances are typically expressed as a percentage, such as ±5% or ±10%.
The following table shows the typical ratings for capacitors:
| Capacitance | Voltage | Temperature | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 pF to 100 µF | 10 V to 1000 V | -55°C to 125°C | ±5% to ±10% |
| 100 µF to 1000 µF | 100 V to 1000 V | -40°C to 85°C | ±5% to ±10% |
| 1000 µF to 10000 µF | 250 V to 1000 V | -25°C to 85°C | ±5% to ±10% |
| 10000 µF to 100000 µF | 500 V to 1000 V | -25°C to 85°C | ±5% to ±10% |
| 100000 µF to 1000000 µF | 1000 V to 2000 V | -25°C to 85°C | ±5% to ±10% |
It is important to select capacitors with the correct ratings for your application. If you use a capacitor with a voltage rating that is too low, it could be damaged or even destroyed. If you use a capacitor with a temperature rating that is too low, it could fail prematurely.
You can find capacitor ratings on the capacitor’s datasheet. The datasheet will also provide information on the capacitor’s other characteristics, such as its ESR, dissipation factor, and leakage current.
Capacitor Selection
Capacitors are used in a wide variety of electrical applications, and the correct capacitor for a given application can vary depending on the specific requirements of the circuit. Some of the factors that need to be considered when selecting a capacitor include:
- The capacitance value
- The voltage rating
- The temperature rating
- The ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance)
- The ripple current rating
- The packaging type
The capacitance value of a capacitor is measured in farads (F), and it determines the amount of electrical charge that the capacitor can store. The voltage rating of a capacitor is the maximum voltage that the capacitor can withstand without failing. The temperature rating of a capacitor is the maximum temperature that the capacitor can operate at without its performance being affected. The ESR of a capacitor is a measure of its resistance to current flow, and it can affect the performance of the capacitor in some applications. The ripple current rating of a capacitor is the maximum amount of alternating current (AC) that the capacitor can withstand without failing. The packaging type of a capacitor refers to the physical size and shape of the capacitor.
When selecting a capacitor for a given application, it is important to consider all of the factors listed above to ensure that the capacitor will meet the specific requirements of the circuit.
Here are some additional resources that you may find helpful:
IX. Capacitor Pricing
The price of a capacitor varies depending on its size, capacitance, and type. Small capacitors, such as ceramic capacitors, are typically less expensive than larger capacitors, such as electrolytic capacitors. Capacitors with higher capacitance are also more expensive than capacitors with lower capacitance.
The following table provides a general overview of capacitor prices:
| Capacitor Type | Size (µF) | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Capacitor | 1 | $0.01 |
| Electrolytic Capacitor | 10 | $0.10 |
| Film Capacitor | 100 | $0.50 |
It is important to note that these prices are just a general guideline. The actual price of a capacitor will vary depending on the manufacturer, the distributor, and the current market conditions.
X. FAQ
Q: What is the function of a capacitor?
A: A capacitor stores electrical energy in an electric field.
Q: What are the different types of capacitors?
A: There are many different types of capacitors, but the most common types are electrolytic capacitors, ceramic capacitors, and film capacitors.
Q: What are the applications of capacitors?
A: Capacitors are used in a wide variety of applications, including power supplies, filters, oscillators, and timing circuits.